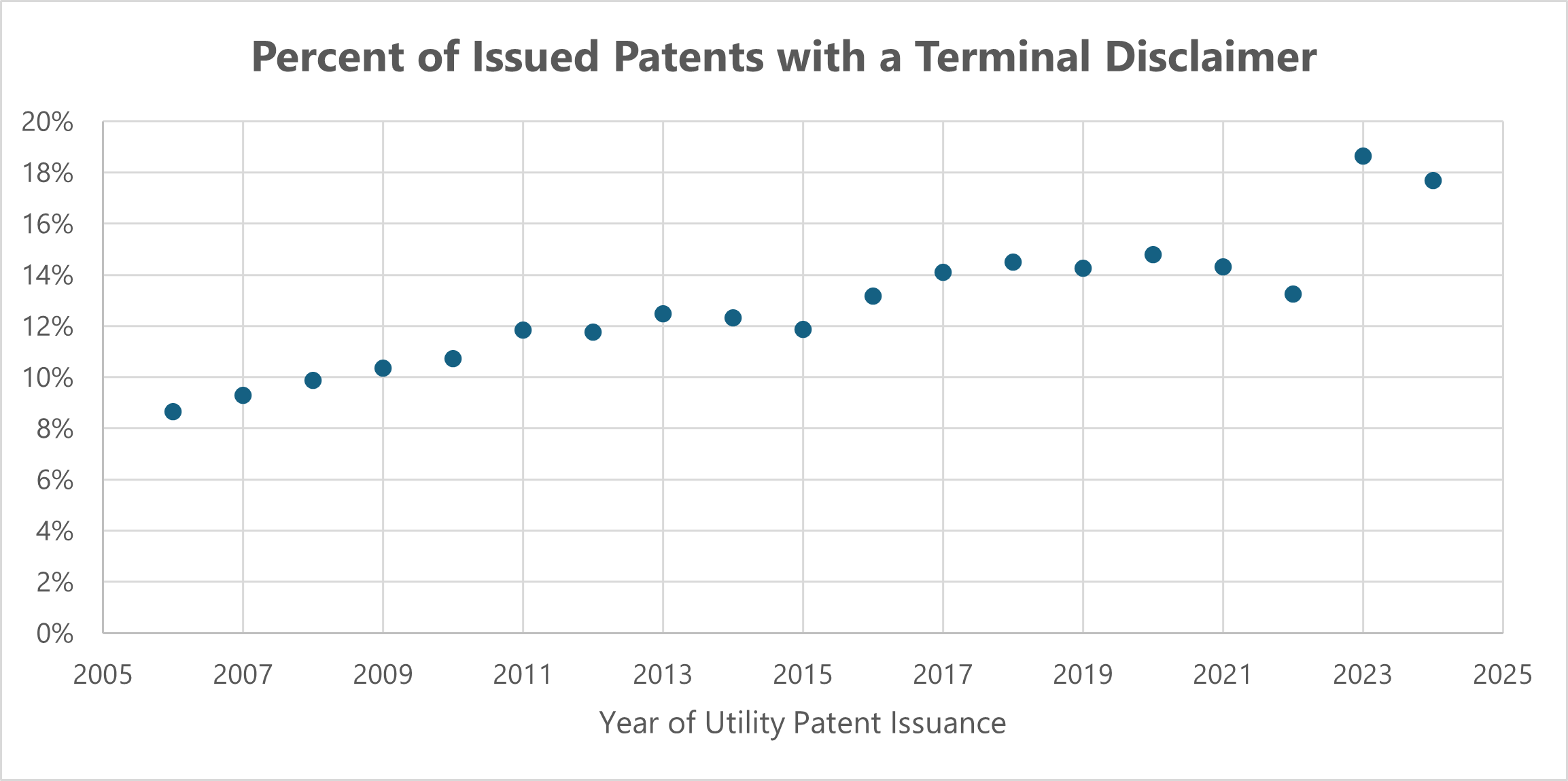
by Dennis Crouch
Speck v. Bates, No. 23-1147 (Fed. Cir. May 23, 2024)
In likely one of the last interference proceeding appeals, the Federal Circuit has applied a "two-way test" to determine whether pre-critical date claims and post-critical date claims are "materially different" under pre-AIA 35 U.S.C. § 135(b)(1). The court found that Bates' post-critical date claims in its U.S. Patent Application No. 14/013,591 were time-barred because they were materially different from Bates' pre-critical date claims.
Although the decision is based upon an interference proceeding, the same provision is found within the new version of 135(b) that covers
To continue reading, become a Patently-O member. Already a member? Simply log in to access the full post.